By Lakshmi Mahadevan, Ph.D.
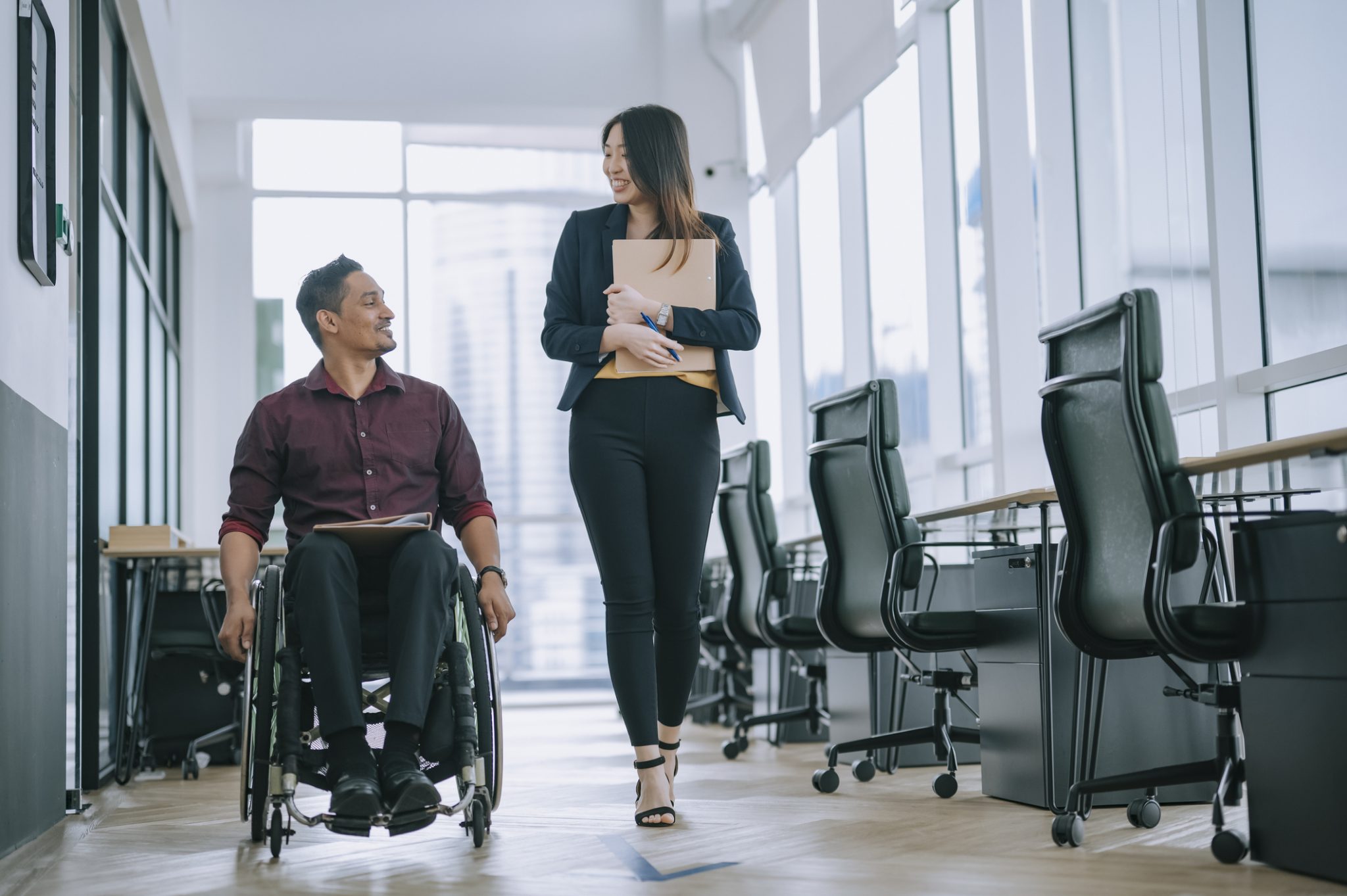
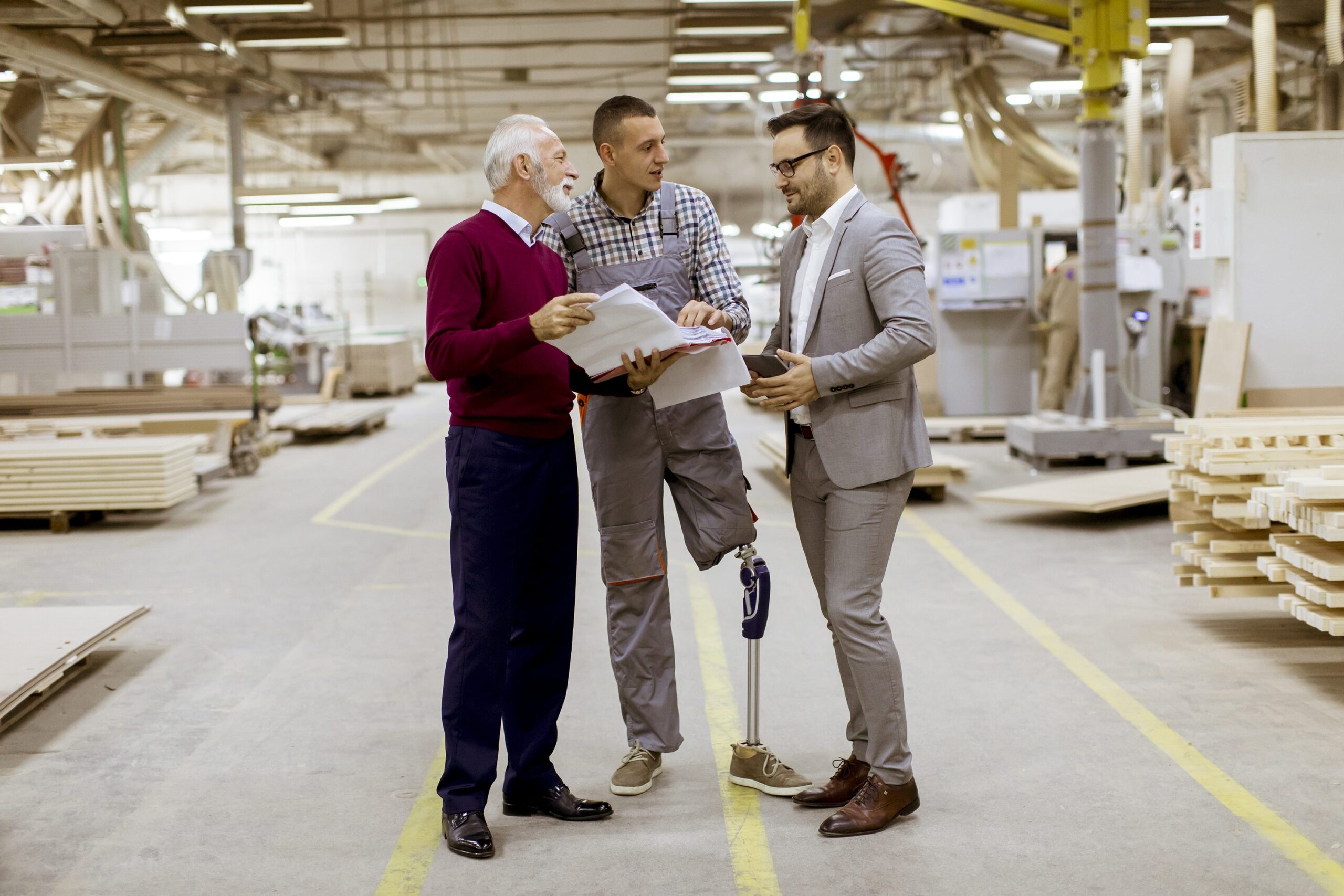
Employers list professionalism as the one of the top skills they need in their new and current employees. What is professionalism? How does an individual with a disability seeking employment or currently employed learn professionalism skills? How can professionalism be maintained throughout one’s career?
According to the Department of Labor, “Professionalism isn’t one thing; it’s a combination of qualities. A professional employee arrives on time for work and manages time effectively. Professional workers take responsibility for their own behavior and work effectively with others. High-quality work standards, honesty, and integrity are also part of the package. Professional employees look clean and neat and dress appropriately for the job. Communicating effectively and appropriately for the workplace is also an essential part of professionalism (Department of Labor, 2022).”
Let’s now closely examine this definition and identify some key skills that will empower individuals with disabilities to learn, develop and maintain professionalism in the workplace.
On Time for Work
- Use an online calendar or paper schedule to organize your day and tasks.
- Plan for 5-minute breaks every 1.5 hrs.
- Use audible and visual timer reminders.
Resource: Time Management Skills: Definition and Examples
Responsibility, Integrity, and Honesty
- Being present for the entire required shift.
- Completing tasks that have been assigned.
- Carry out the specific duties that go along with the job.
- Doing the right thing in a reliable way.
Work Effectively with Others
- Respect, be open to and supportive of the thoughts, opinions, and contributions of others in the group.
- Recognize and respect people’s diversity, individual differences, and perspectives.
- Accept and provide feedback in a constructive and considerate manner.
Resource: What is respect in the workplace?
Appearance
- Wear clothes appropriate for the job.
- Find out and follow workplace dress code and protocol regarding body piercing, tattoos, etc.
- Maintain good hygiene.
Resource: A Quick Guide to Professional Dress for Men and Women
Communication
- Ask appropriate questions.
- Listen for issues or problems that recur.
- Paraphrase what is heard to clarify understanding.
- Learn that all conversations are:
- Cautious even in an informal setting
- Considered formal unless speaking to work friends.
- Considered confidential unless it applies to the whole group.
Self-Advocacy
In addition to the above employees with disabilities must learn to self-advocate by:
- Choosing not to self-disclose.
- Practice asking for appropriate job accommodations.
- Discussing safety needs.
- Communicating with superiors and planning for job growth and advancement.
Resource: Best Practices in Self-Advocacy Skill Building
Managing Emotions
Individuals with disabilities must also plan to deal effectively with emotions that may occur in correspondence with searching for, getting, and succeeding in the job. Skills that can be developed to manage emotions include:
- Taking a time-out when appropriate (from a conversation, from a task, etc.)
- Find a quiet space to practice recognizing negative thoughts/feelings and naming them.
- “I am upset.”
- “I am angry.”
- “I am furious.”
- “I am disappointed.”
- “I am sad.”
- Practice techniques to minimize the impact of your feelings – deep breathing, drink a beverage, look out the window or walk outside.
Resource: Stress Management
Techniques to Learn and Maintain Professionalism
- Talk to family and friends about their job-related experiences and skills they practice.
- Watch online videos that portray job seekers’ activities such as resume writing and interviewing.
- Roleplay and practice communicating in an “employee’s” language.
- Do internet research to identify resources for learning about and developing skills that employers want.
- Practice emotion control and manage anxiety by using a breathing technique – breath in deep to a count of 4 seconds, hold and let out for a count of 8 seconds.
Additional Resources: