By Rachel Brauner
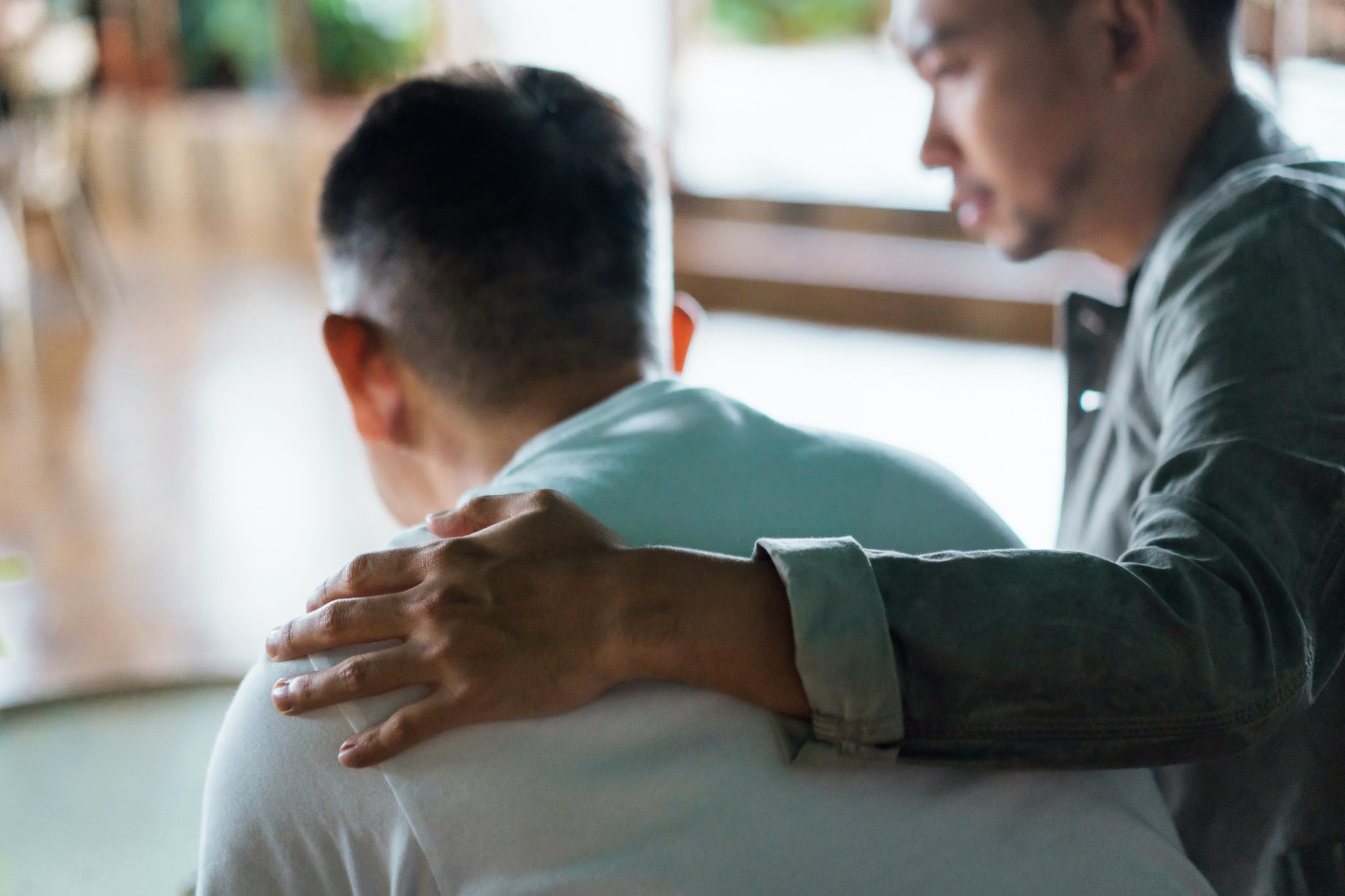
The negative impact of traumatic events can extend beyond those who directly experienced the trauma to caregivers who are subject to secondary traumatic stress. Secondary trauma, also known as vicarious trauma or compassion fatigue, is a condition where individuals who are exposed to the traumatic experiences of others can develop their own trauma-related symptoms. Military caregivers, who provide care and support to military personnel who have experienced trauma during their service, are particularly vulnerable to secondary trauma.
Symptoms of Secondary Trauma
The experience of secondary traumatic stress can lead to impairment in social and occupational functioning and can manifest in a variety of ways. Some of the common symptoms of secondary trauma include:
- Emotional distress: Military caregivers may experience intense emotions such as anxiety, depression, anger, guilt, and sadness as a result of being exposed to the trauma experienced by the military personnel they are caring for.
- Physical symptoms: The stress of caregiving can cause physical symptoms such as fatigue, insomnia, headaches, and stomach problems.
- Avoidance behaviors: Military caregivers may try to avoid situations or people that remind them of the traumatic experiences of the military personnel they are caring for.
- Loss of empathy: Over time, military caregivers may become desensitized to the trauma experienced by the military personnel they are caring for, which can lead to a loss of empathy and a reduced ability to connect with others emotionally.
- Strained relationships: The stress of caregiving and the symptoms of secondary trauma can strain relationships with family members, friends, and colleagues.
It is important to note that not all military caregivers will experience secondary trauma, and those who do may experience different symptoms to varying degrees. However, it is important for military caregivers to be aware of the risk of secondary trauma and to seek support if they experience symptoms.
Tips for Caregivers
There are several ways that military caregivers can manage the impact of secondary trauma, including:
- Seeking support: Military caregivers can seek support from family members, friends, and mental health professionals who can provide emotional support and help them to manage their symptoms.
- Self-care: Engaging in self-care activities such as exercise, relaxation techniques, and hobbies can help military caregivers to manage stress and reduce symptoms of secondary trauma.
- Education: Learning about the symptoms of secondary trauma and how to manage them can help military caregivers to recognize and address their own symptoms.
- Connecting with other caregivers: Connecting with other military caregivers who have experienced similar challenges can provide a sense of community and support.
Overall, secondary trauma can have a significant impact on military caregivers, but there are steps that can be taken to manage symptoms and support the well-being of those who provide care to military personnel. To learn more about the concept of secondary traumatic stress, symptoms, and additional strategies to minimize the negative impact of secondary traumatic stress go to – Risk and Resilience: Understanding Secondary Traumatic Stress Post-Pandemic.