Written by: Rachel Brauner, Program Coordinator, OneOp Lifespan Caregiving
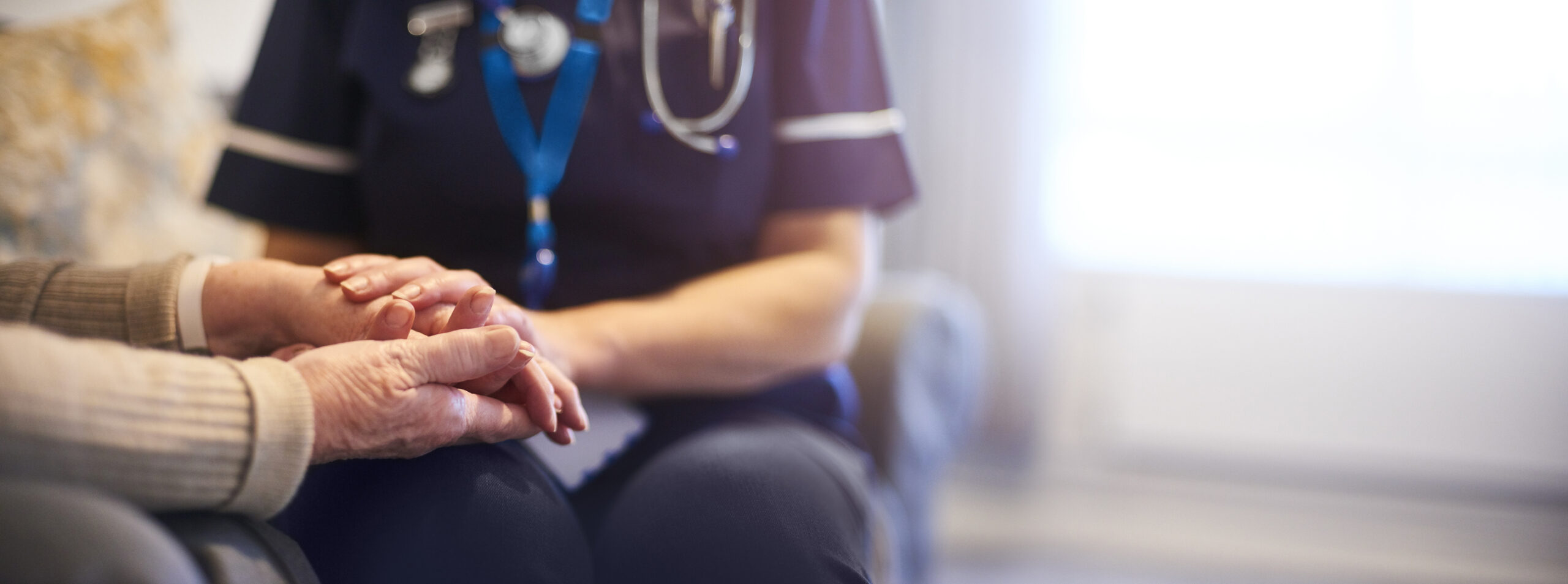
When navigating the complexities of serious illness, it’s crucial to understand the various care options available. Two terms that often come up are “palliative care” and “hospice care.” While they share similarities in their goals of providing comfort and support, they are distinct in several important ways. This article aims to clarify the differences between palliative care and hospice care, helping providers, patients, and families make informed decisions about their healthcare needs.
What is Palliative Care?
Palliative care is a specialized medical approach focused on improving the quality of life for patients dealing with serious, chronic, or life-threatening illnesses. It can be provided at any stage of the illness, alongside curative treatments.
Key Features of Palliative Care
Palliative care is characterized by several key features that enhance the quality of life for patients with serious illnesses. At the forefront is symptom management, where palliative care aims to relieve pain, nausea, fatigue, and shortness of breath, enhancing the patient’s comfort and overall well-being. This approach is holistic, addressing not only physical symptoms but also the emotional, psychological, and spiritual needs of patients, ensuring comprehensive care.
A significant aspect of palliative care is its patient-centered nature. The care provided is tailored to the individual’s specific needs, preferences, and goals, involving patients and their families in the decision-making process to ensure that their wishes are respected. Additionally, palliative care teams offer various supportive services, including counseling, social support, and assistance navigating the healthcare system, which helps patients, and their families manage the complexities of serious illness.
Importantly, palliative care can be integrated with curative treatments such as chemotherapy, radiation, or surgery. This means that patients do not have to choose between seeking a cure and receiving comfort care; they can have both simultaneously, optimizing their quality of life at every stage of their illness.
What is Hospice Care?
Hospice care is a type of palliative care specifically designed for patients who are nearing the end of life. It is generally reserved for those who are no longer seeking curative treatments and have a prognosis of six months or less to live.
Key Features of Hospice Care
Hospice care is characterized by several key features that distinguish it from other forms of medical care, particularly in its focus on the end of life. Primarily, hospice care centers on providing comfort and support during the final stages of life, emphasizing quality of life over the extension of life. This approach includes comprehensive support that encompasses medical, emotional, spiritual, and practical needs for both patients and their families, ensuring that all aspects of their well-being are addressed.
An interdisciplinary team delivers hospice care, consisting of healthcare professionals such as doctors, nurses, social workers, chaplains, and volunteers. This collaborative approach ensures that patients receive well-rounded care from specialists in various fields. Additionally, hospice care is often provided in the patient’s home, allowing them to stay in a familiar and comfortable environment, although it can also be administered in hospitals or hospice centers.
Beyond the immediate care for the patient, hospice care also extends support to families after the patient’s death through bereavement services. This includes offering grief counseling and other resources to help families cope with their loss, providing them with much-needed support during a difficult time.
Key Differences Between Palliative Care and Hospice Care
Understanding the key differences between palliative and hospice care is crucial for making informed healthcare decisions. Timing and eligibility are primary distinctions: Palliative care is available at any stage of a serious illness and can be provided alongside curative treatments, whereas hospice care is reserved for patients in the final stages of life, typically with a prognosis of six months or less, who have decided to forgo curative treatments.
The goals of care also differ. Palliative care aims to improve quality of life by managing symptoms and providing holistic support, regardless of the stage of the illness or the patient’s treatment goals. In contrast, hospice care focuses on comfort and quality of life at the end of life, prioritizing symptom relief and emotional support over curative treatments.
The settings in which these services are provided vary as well. Palliative care can be administered in hospitals, outpatient clinics, nursing homes, or at home, offering flexibility based on the patient’s needs. Hospice care, however, is commonly provided in the patient’s home to allow them to remain in a familiar and comfortable environment, although it is also available in hospice centers, hospitals, and long-term care facilities.
Finally, insurance coverage for these services differs. Palliative care is often covered by private insurance, Medicare, and Medicaid, similar to other medical services. Hospice care is typically covered under Medicare, Medicaid, and most private insurance plans, with specific benefits designed for end-of-life care. Understanding these distinctions helps patients and families choose the most appropriate care based on their particular circumstances and needs.
Conclusion
While palliative and hospice care prioritize comfort and quality of life, they serve different purposes and are appropriate at different stages of illness. By knowing these distinctions, providers, patients, and families can better navigate their options and ensure they receive the support that best meets their needs. If you know of someone facing a serious illness, consider discussing these options with your healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate care plan. Both palliative and hospice care can provide invaluable support, ensuring dignity and comfort during challenging times.
References
Connor, S. R. 2009. What are hospice and palliative care? In Hospice and palliative care: the essential guide (pp. 17–34). Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203886151-5
National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization. 2024. Explanation of Palliative care | NHPCO. NHPCO. https://www.nhpco.org/palliativecare/explanation-of-palliative-care/
*Image Source: 1129903329, MartinPrescott