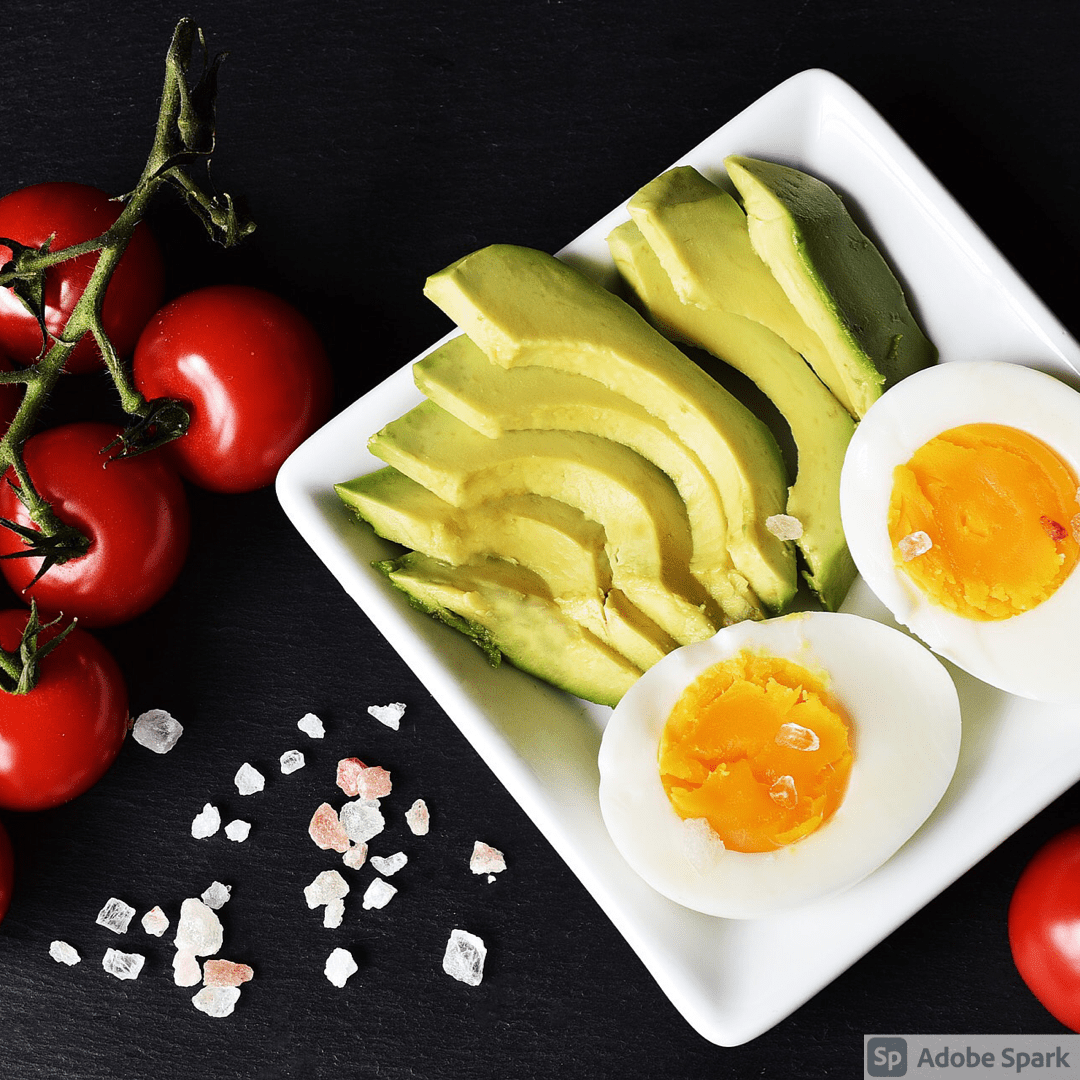
“Fat is the enemy” has continued to be the popular one-size-fits-all diet advice in the media when it comes to health and nutrition. Yet, the recent popularity of the keto diet has flipped these nutritional suggestions of demonizing fat on its head.
Although the keto diet and lifestyle can seem confusing, there are some handy pointers that can make following the keto diet a little easier.
Where to Begin
“Low-carbohydrate and high-fat” are a vague set of directions. How high is high? And how low is low? For starters, there is no “golden ratio” or fixed number of macronutrients that applies to everyone (Kirkpatrick et al., 2019). Like many diet and lifestyle choices, needs and adjustments are personal.
Some variations of the keto diet: (Mohan & Shilpa, 2018)
- Standard ketogenic diet: 70% of intake is fat, 20% is protein, and 10% is carbs.
- Cyclical ketogenic diet: A cycle of 5 low carb days and 2 high carb days.
- Targeted ketogenic diet: A person can eat more carbs around high-intensity workouts.
- High protein ketogenic diet: 60% of intake is fat, 35% is protein, and 5% is carbs.
Though many versions of the keto diet can exist, all forms follow the pattern of high-fat, low-carb, and moderate protein. Make sure to speak with a dietitian to find the methods of eating keto that work the best for you.
Food Guidelines for Keto
Emphasize: (Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, 2019); (Mayo Clinic, 2020)
- Fats at each meal and snacks that meet the high-fat requirement.
- Focus on unsaturated fat sources.
- Use fats like olive, palm, and coconut oil for cooking.
- Avocados, coconut meat, walnuts, and pumpkin seeds.
- Low lactose dairy foods.
- Butter and hard cheeses.
- Moderate protein intake.
- Grass-fed beef, free-range poultry, wild-caught fish, eggs, and tofu.
- Non-starchy vegetables.
- Cauliflower, broccoli, brussels sprouts, bell peppers, onions, mushrooms, cucumber, celery, kale, spinach, and lettuce.
- Low carbohydrate fruits in small portions.
- Strawberries, blackberries, raspberries.
- Unsweetened beverages
- Unsweetened vinegar and mustards, herbs, and spices can be used to flavor meals.
Minimize: (Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, 2019); (Mayo Clinic, 2020)
- All whole and refined grains and flour products.
- White bread and pasta, cereals, cake, and cookies.
- High lactose dairy
- Ice cream and full-fat milk.
- Added and natural sugars
- Starchy vegetables
- Potatoes, corn, and winter squash.
- High carbohydrate fruits and fruit juices.
- Bananas, grapes, apples, and pears.
- Legumes
- Beans, lentils, and peanuts.
- Full carbohydrate wines and beer, and drinks with added sweeteners
- Cocktails, mixers with syrups and juice, and flavored alcohols.
Summary
Choosing to follow a high-fat diet like keto can be difficult at first, but making small adjustments to your daily routine is a great start. It can be as simple as adding an avocado to your meals or replacing your morning toast with eggs. While the keto diet may not be for everyone, understanding the choices available with keto will be helpful in finding a diet that can support your needs.
References:
- Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. (2019). Diet Review: Ketogenic Diet for Weight Loss. Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. Retrieved 15 July 2021, from https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/healthy-weight/diet-reviews/ketogenic-diet/.
- Kirkpatrick, C., Bolick, J., Kris-Etherton, P., Sikand, G., Aspry, K., & Soffer, D. et al. (2019). Review of current evidence and clinical recommendations on the effects of low-carbohydrate and very-low-carbohydrate (including ketogenic) diets for the management of body weight and other cardiometabolic risk factors: A scientific statement from the National Lipid Association Nutrition and Lifestyle Task Force. Journal Of Clinical Lipidology, 13(5), 689-711.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacl.2019.08.003
- Mayo Clinic. (2020). Can a low-carb diet help you lose weight?. Mayo Clinic. Retrieved 16 July 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/weight-loss/in-depth/low-carb-diet/art-2004583
- Mohan, V., & Shilpa, J. (2018). Ketogenic diets: Boon or bane?. Indian Journal Of Medical Research, 148(3), 251. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijmr.ijmr_1666_18